Height Of Aircraft Carrier - Shandong was built by Dalian Shipbuilding Industry in 2018. The aircraft carrier, which is also known as Type 002, was commissioned in 2019. While Shandong is the first Chinese-made aircraft carrier, it is a variant of the Soviet-built Kuznetsov-class
aircraft carrier. Other nations and light carriers. The United States has decommissioned about as many carriers—63—as the rest of the world had afloat in 2003. Nations with carriers included the United Kingdom, France, Russia, China, Italy, Japan, Spain, India, Brazil, Chile, Peru
Height Of Aircraft Carrier
, China, and Thailand. The leading carrier power, other than the United States, was—not surprisingly, given the many previous British achievements in carrier design—the United Kingdom. In part to facilitate the building of smaller and more economic carriers, the British in the late 1960s developed the Harrier jet, which takes off almost vertically.
Overview Of A Modern Carrier
As of 2003, its fleet included three small carriers of the Invincible class, built for vertical/short takeoff and landing (V/STOL), each capable of carrying eight Harriers and from 10 to 12 helicopters. Members of a battle group may include at least one destroyer and one frigate, two attack submarines, two guided missile cruisers, one guided missile destroyer, and a logistical support ship.
Destroyers and frigates are primarily for anti-submarine warfare, while attack submarines, as their name implies, attack both enemy submarines and ships. Both guided missile cruisers and destroyers are multi-mission surface combatants, the first type armed with Tomahawk cruise missiles for long-range strike capability, and the second equipped for anti-aircraft warfare.
The logistical support ship is usually a combined ammunition, oiler, and supply vessel. Other notable naval powers include Italy, which had six carriers, helicopter carriers, or amphibious assault ships either in operation or under construction in 2003. These included the Andrea Doria, scheduled for completion in 2007. Built along the V/STOL model, the Andrea
Doria would hold eight Harriers or 12 helicopters. Other navies with aircraft carriers, helicopter carriers, helicopter destroyers, or amphibious assault ships included Japan, Brazil, India, Spain, Thailand, and Peru. With the launch of its 59th carrier, Forrestal, in 1959, the United States introduced the era of the very large carrier.
Components In The Carrier Concept
The Forrestal included rectangular extensions on the rear part of the flight deck, which greatly expanded the deck area. Designers had also moved the elevators off to the side, so that they could be used even as aircraft were taking off and landing.
Unlike the old oil-boiler carriers, modern nuclear carriers do not have to refuel regularly. In fact, they can go 15 to 20 years without refueling. The trade-offs are a more expensive power plant, a longer, more complicated refueling process (it takes several years) and the added risk of a nuclear disaster at sea.

To minimize the risk of such a catastrophe, the reactors inside a supercarrier are heavily shielded and closely monitored. U.S. aircraft carriers fall into several groupings, the largest of which is the Nimitz class. Largest warships in the world, these measure 1,092 feet (332.9 m) from bow to stern, and 252 feet (76.8 m) across.
As large as it is, the large U.S. carrier still does not provide enough room for takeoff and landing by conventional means; therefore, the carrier deck includes a number of items for these purposes, as well as for the storage of aircraft below decks.
Evolution Of The Carrier
Primary Flight Control, or "Pri-Fly," is the control tower for flights. Above it on the "island," the part of the carrier that sticks up above the flight deck, is the bridge, the command and control center of the carrier as a whole.
On the bridge is always an officer of the deck (OOD), designated by the ship's commanding officer, who serves a four-hour watch. The OOD is responsible for all aspects of the safety and operation of the ship, among which are navigation, ship handling, communications, and routine tests, and inspections.
Also on the bridge are the helmsman, who steers the ship, and numerous other personnel. Two years later, in 1961, the Navy introduced the first nuclear-powered carrier, the Enterprise. It is no accident that the world's most well-known fictional spaceship, from the 1960s television show Star Trek, was also called the Enterprise.
During that era, the standard of excellence among carriers—the epitome of technological superiority anyone was likely to encounter in real life—was the Enterprise, which carried 100 aircraft, displaced 75,700 tons (68,674 tons), and moved at speeds higher than 30 knots.
(55.6 kph). With eight nuclear reactors, it could travel for three years before being replaced. As of 2003, the United States had launched a total of 75 carriers, with two more under construction. Its 12 active carriers included the Enterprise and the Kitty Hawk class (the Kitty Hawk and Constellation), all launched in 1961;
the John F. Kennedy, launched in 1968; and eight carriers of the Nimitz class: Nimitz, Dwight D. Eisenhower (1977), Carl Vinson (1982), Theodore Roosevelt (1986), Abraham Lincoln (1989), George Washington (1992), John C. Stennis (1995), and Harry S. Truman (1998).

Additionally, the Ronald Reagan was under construction, with launch planned for the middle of the decade, while construction was to begin on the George H. W. Bush, with completion planned for 2009. (Both are Nimitz-class carriers.)
Admiral Kuznetsov was built by Nikolayev South during the Soviet era. First commissioned in 1991, the aircraft carrier is currently the only unit operated by the Russian Navy. As of June, Admiral Kuznetsov is undergoing a refit, per the wire agency Reuters.
Built by Cochin Shipyard Limited, the INS Vikrant is the first-ever aircraft carrier constructed in India. Launched in 2013, the ship's construction cost over $3.5 billion and was originally scheduled for commissioning in 2018 but was delayed due to the pandemic.
aircraft carrier Military vessel with a wide open deck that serves as a runway for the launching and landing of aircraft. A modern nuclear-powered carrier may have a flight deck c.300m (1000ft) long, a displacement of c.75,000 tons, a 4000-man crew, and carry 90 aircraft of various types.
Some carriers have large, angled decks to permit launching and landing simultaneously. Local media describe the INS Vikrant as an "elite" warship. The aircraft carrier is slated to operate MiG-29K fighter jets, Kamov-31 helicopters, and Sikorsky MH-60R Seahawk helicopters once commissioned in September, per local news site India Times.
The carrier is one of the leading means for force projection, or the ability to project an aggregation of military personnel from the continental United States (or another theater) in response to military requirements. As long as it operates in international waters, a carrier needs no permission to conduct landings or overflights.
These floating military bases constitute sovereign U.S. territory capable of moving over the oceans—70% of Earth's surface—in the service of U.S. interests. There are 47 aircraft carriers currently in active service in the world — all of which are operated by just 14 countries.
Aircraft carriers are considered the "most valuable" naval asset, tasked with not just war operations but guarding territorial waters, per a 2020 report from the Joint Air Power Competence Center. Stefan Terzibaschitsch, Aircraft Carriers of the U.S.

Navy, 1980. Norman Friedman, Carrier Air Power, 1981. Stefan Terzibaschitsch, Escort Carriers and Aviation Support Ships of the U.S. Navy, 1981. Norman Friedman, U.S. Aircraft Carriers: An Illustrated Design History, 1983. Clark G. Reynolds, The Fighting Lady: The New Yorktown in the Pacific War, 1986. George C. Wilson, Supercarrier, 1986. Edward P. Stafford, The Big E, 1988 repr.
Clark G. Reynolds, The U.S. Fleet‐in‐Being Strategy of 1942, The Journal of Military History, Vol. 58 (1994), pp. 103–118. Theodore Taylor, The Magnificent Mitscher, 1991 repr. Postwar changes. By the end of World War II, the United States had commissioned more than 34 carriers, with several more made operational late in 1945. But it had also lost several such vessels, including the first two, the Langley and the Lexington.
Following the war, the introduction of guided missiles revolutionized the nature of the carrier battle group, while nuclear fission replaced diesel power for the most advanced carriers. Five countries — US, China, UK, France and India — operate 10 of the world's largest aircraft carriers in terms of displacement.
According to naval architect Harry Alexander Karanassos, displacement refers to the mass of water displaced by a ship. With a total of 10 planned aircraft carriers, the Gerald R. Ford-class is regarded as the US Navy's warships of the future.
The USS Gerald R. Ford, the first aircraft carrier to be built, was commissioned in 2017. The research and development of the class cost $37.3 billion, and the construction of each unit cost almost $13 billion.
Fujian is fitted with catapults that can launch "larger and heavier aircraft," according to the Hong Kong-based news site Asia Times. The aircraft carrier is tasked with reinforcing Chinese presence on the eastern side of Taiwan, the publication reported, citing local naval strategists.
Carriers figured heavily in World War II, particularly during operations in the Pacific theater. The Japanese launched their attack on U.S. forces at Pearl Harbor in December, 1941, from carriers, and in May, 1942, the United States struck back decisively in the Battle of the Coral Sea, the first naval battle in which opposing fleets fought without their ships coming in sight of each other
. A month later, the Battle of Midway proved one of the turning points in the war, and reinforced the concept of naval air support. There are 10 aircraft carriers that belong to the Nimitz-class. All were built by Newport News Shipbuilding.
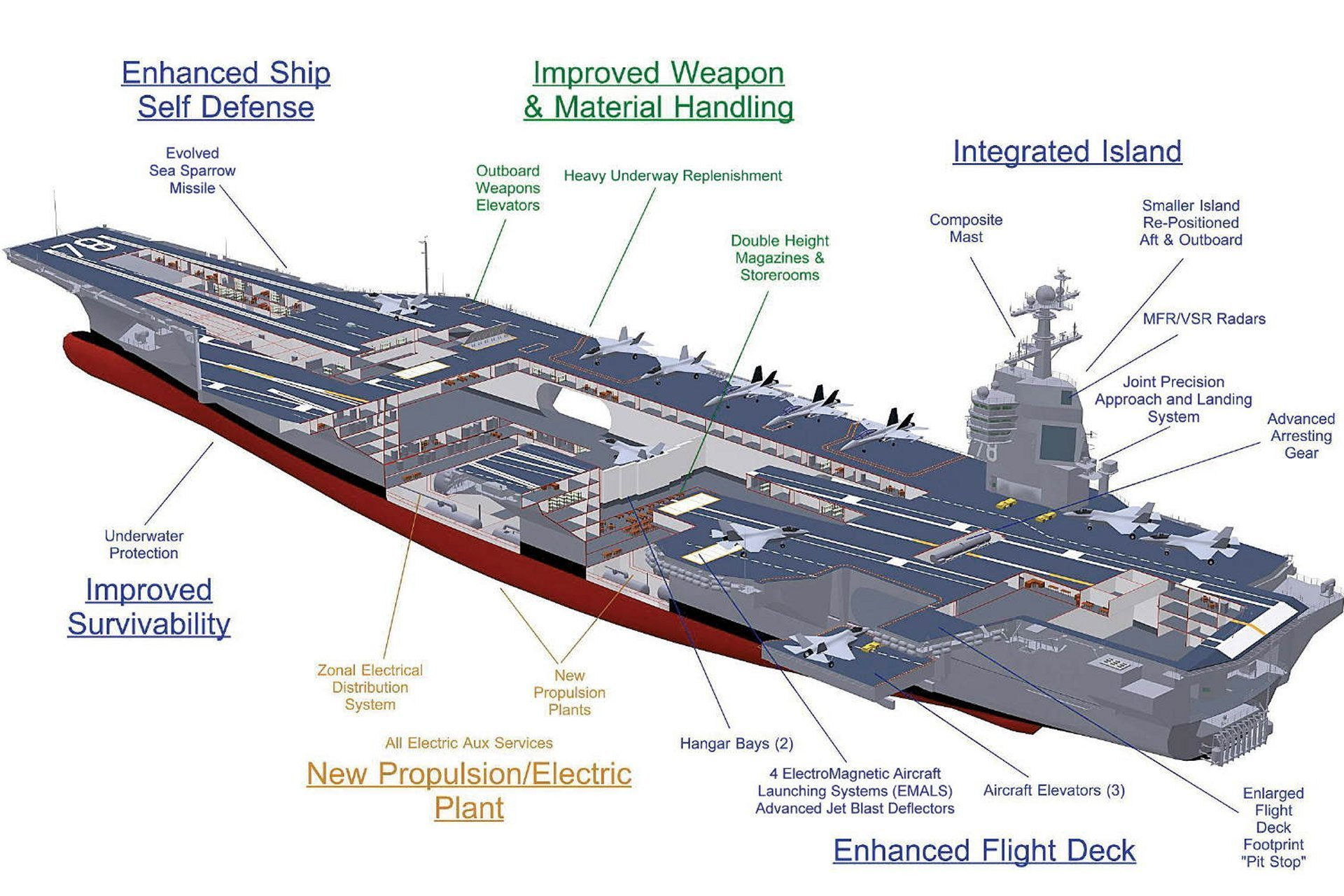
The first aircraft carrier in the class, USS Nimitz, was commissioned in 1975 but is due to be decommissioned in 2025. The INS Vikramaditya is a Soviet-made aircraft carrier that was commissioned by the Indian Navy in 2013, per the navy's official website.
The warship is regarded as the current flagship of the navy, and was purchased from Russia for $2.35 billion. As impressive as it was, the Enterprise would be eclipsed by the Nimitz (commissioned in May 1975) and the rest of its class.
Instead of eight reactors, these required only two, whose uranium cores needed to be replaced once every 13 years. The carriers displaced 81,600 tons, but had much smaller propulsion systems, and thus, could store much more aircraft fuel.
The carrier's two nuclear reactors, housed in a heavily-armored, heavily restricted area in the middle of the ship, generate loads of high-pressure steam to rotate fan blades inside the turbine. The fans turn the turbine shaft, which rotates the screw propellers to push the ship forward, while massive rudders steer the ship.
The propulsion system boasts something in excess of 280,000 horsepower (the Navy doesn't release exact numbers). The INS Vikrant has a projected displacement of 45,000 tons which will make it the Indian Navy's largest aircraft carrier, superseding the INS Vikramaditya.
It measures 860 feet in length and 194 feet in height and can accommodate a crew of 1,645. Because each style has its own formatting nuances that evolve over time and not all information is available for every reference entry or article, Encyclopedia.com cannot guarantee each citation it generates.
Therefore, it's best to use Encyclopedia.com citations as a starting point before checking the style against your school or publication's requirements and the most recent information available at these sites: Carriers make possible a variety of options.
They may be used to insert forces ashore; on the other hand, their presence is so intimidating that they may be used simply to "show the flag," or remind hostile powers of the U.S. presence. They are capable of attacking airborne, sea borne, or land targets, and engage in sustained operations in support of other forces—for example, the ground forces deployed for Operation Iraqi Freedom in 2003.

Sometimes characterized as "floating cities," aircraft carriers are a potent symbol of America's strength as a superpower. Although nations ranging from the United Kingdom and Russia to Peru and Thailand have their light carriers and helicopter carriers, the large carriers of the United States are without parallel in ability and firepower.
Carriers provide an important means of force projection from the continental United States to any theater, no matter how hostile, and offer a floating platform for missions that include both combat and intelligence-gathering. As President William J. Clinton said during a visit to the carrier Theodore Roosevelt in the 1990s, "When word of crisis breaks out in Washington, it's no accident that the first question that comes to everyone's lips is, 'where is the nearest carrier?
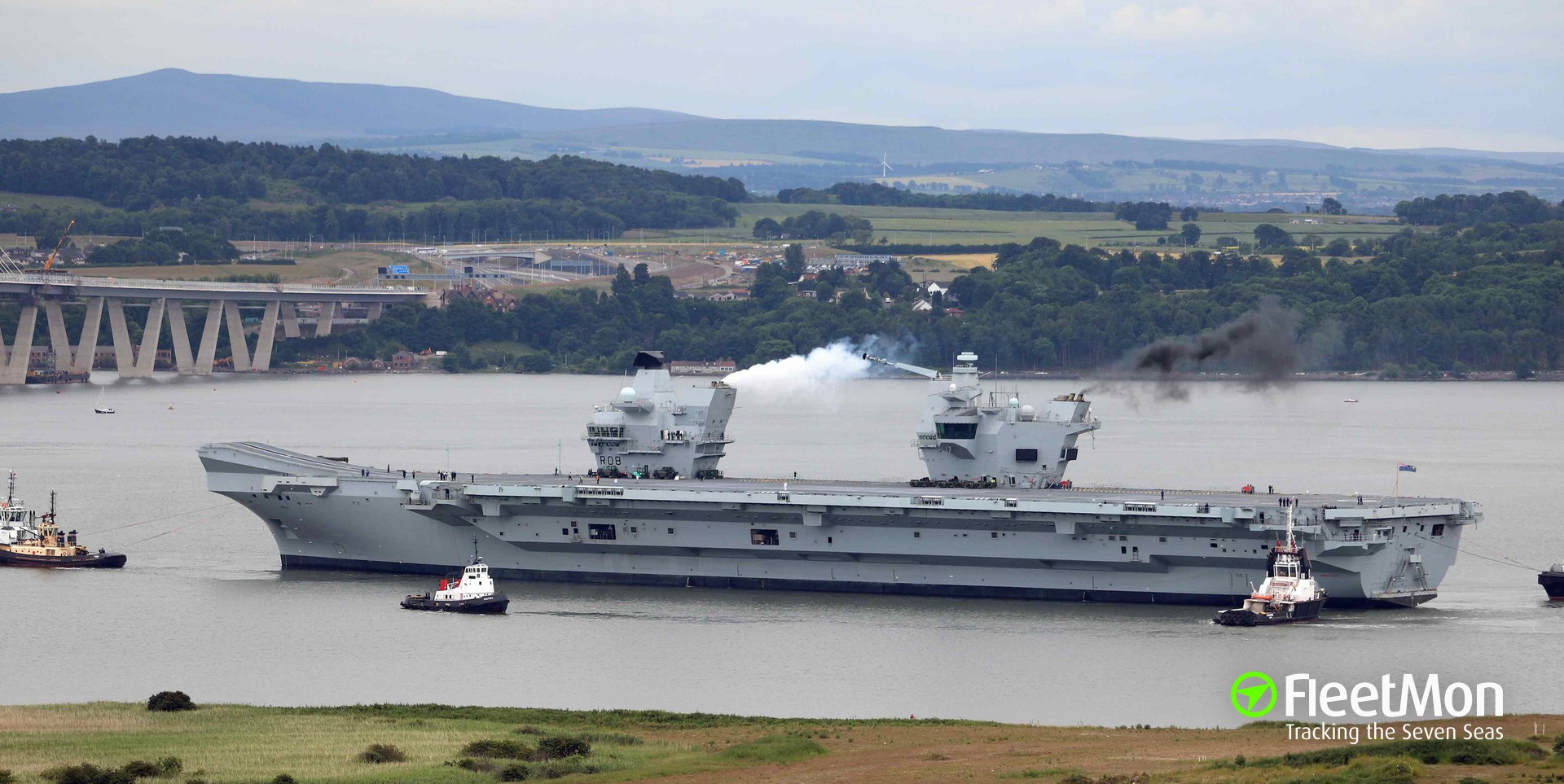
'" HMS Queen Elizabeth is equipped with armament that includes the Phalanx close-in weapon system and US-made M134 miniguns. It can carry more than 65 aircraft, which includes the Lockheed Martin F-35 fighter jet and the Boeing Chinook helicopter.
night surveillance, electronic countermeasures, command/control/communications warfare, and search and rescue; one squadron of EA-6B Prowlers, which jams enemy radar, electronic data links, and communications; one squadron of E-2C Hawkeyes, all-weather tactical warning and control system aircraft;
and one squadron of SH-60 Seahawks, twin-engine utility or assault helicopters. Before placing a superlift module into the ship, the construction crew assembles its steel body and hooks up almost all wiring and plumbing. Then they use a giant bridge crane to lift the module and lower it precisely into its proper position inside the ship;
then they weld it to the surrounding modules. Near the end of construction, the crew joins the last module, the 575-ton island, to the flight deck. Powered by two nuclear reactors with four geared steam turbines and four shafts, the Nimitz-class carrier is capable of spending at least half a year at sea, and more than a decade without refueling.
Its ship's company exceeds 3,000, with almost 2,500 more on the air wing. Below decks is an entire city, complete with vast warrens of living spaces, dining halls that serve nearly 20,000 meals a day, a radio and television station, a barber shop, a library, gymnasium, a hospital and dentist office, shops, and a
post office. HMS Queen Elizabeth is a class that includes two aircraft carriers, the HMS Queen Elizabeth and the HMS Prince of Wales. The lead ship, HMS Queen Elizabeth, was commissioned in 2017. The class was built by the Aircraft Carrier Alliance and cost around £3.8 billion to construct per unit.
aircraft carrier height above water, aircraft carrier lengths, dimensions of an aircraft carrier, us aircraft carrier sizes, how tall are aircraft carriers, size of aircraft carrier, list of us aircraft carriers, current us aircraft carriers in service